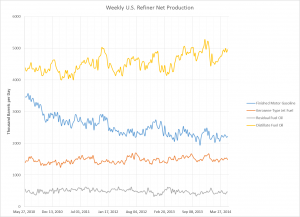
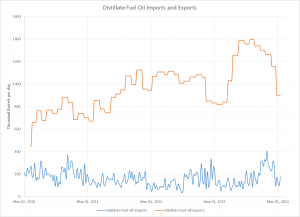
The most notable change in the supply of petroleum fuels for the United States is the drastic growth in domestic production of both natural gas and crude oil. The development of production in tight formations, or shale formations (particularly the now well-known Marcellus Shale in the Northeastern United States) combined with the technological advances (hydraulic fracturing and directional drilling), has had far-reaching effects, including decreased both dependency on and imports from other countries. The largest change is from Africa, with imports from that region decreasing by 90% from 2010 to 2014. For comparison, 2008 tight oil production accounted for only 12% of US production, while in 2012 the number rose to 35%. By 2019, we can expect half of US oil production to be from tight oil formations. This increased domestic production has also reduced costs, allowed prices to decrease, and making natural gas a viable and inexpensive alternative to coal in the generation of electricity. While increased use of natural gas in the electricity generation sector is partially environmental policy-driven, much of this growth can be attributed to the mechanics of a price competitive market. This change is beneficial, as when comparing these two sources of energy, combustion of natural gas produces far less carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur emissions than coal. Natural gas also does not contain harmful particulate matter such as mercury. Furthermore, there have also been advances in other renewable sources of energy including wind and solar power. As these sources become more competitive as costs decrease, we can expect renewable electricity generation to account for 16% of total electricity generation in the United States by 2040.
There have been many positive changes regarding the environmental concerns from combustion of petroleum fuels in internal combustion engines. Though the total miles driven and vehicles used have increased (total vehicle miles traveled increasing by 0.9% each year), it has been more than offset by the increased fuel efficiency of engines. Strict regulations and standards set in place have forced manufacturers to develop better and cleaner vehicles. The EIA website states that light-duty vehicle fuel efficiency has increased by nearly 2% each year, and can be expected to reach 37.2 miles per gallon by 2040 from 21.5 mpg in 2012. Additionally, the entire nation has been slowly and gradually moving towards diesel fuels, biofuels, hybrid, and completely electric cars (most notably Tesla, with massive growth in recent years). Overall, I believe that the United States is moving in the right direction with regards to environmental policy and sustainability. However, this is a global issue and countries such as China and India must also follow suit (though India’s new prime minister has stated that the entire country will be moving towards solar powered homes, hoping that each home is powered by the year 2019).